Whether you are a giant corporation or a startup, to be successful, it is important to analyse if you are compliant and are following certain laid-down protocols. It's imperative to keep a close eye on the laws in the city or state you operate in, failing which you are likely to overlook compliance responsibilities and face damaging penalties and lawsuits that could severely impede the progress of your business entity.
Organisations that have shown a great deal of promise have had founders step down, executives replaced, and employees lost due tobypassing important compliance procedures. A business entity that is compliant is automatically trustworthy to its clients and investors.

Image: shutterstock
All businesses, particularly startups, should follow certain compliance protocols. This article will give you a lowdown on all compliances.
1) Choosing the right business entity
Choosing the right business vehicle for their venture is a major challenge faced by any entrepreneur. This choice will in the near and long term affect the startup's viability, visibility, sustainability, suitability, and profitability. Your long-term goals, vision, and objectives will decide whether the startup will be established as a private limited company, public limited company, partnership firm, or a limited liability partnership.
Each of these categories has a different set of compliance procedures and laws. To avoid any backfiring in the form of legal hassles or otherwise, it is better to be aware of all these formalities right at the inception stage.
2) Statutory compliances
The credibility of any business highly depends on its compliance with all the applicable laws. For a Company and LLP, the mandatory compliances with the Registrar of Companies (RoC) are the most essential of all. Some of the important provisions include appointment of auditor, conducting board and shareholder’s meetings, filing statutory annual returns, and maintenance of statutory registers. These criteria should be met and will be verified by the investors.
a) Appointment of auditors
The first auditors of a company should be appointed within one month of its incorporation and shall hold office till the conclusion of the first annual general meeting. Thereafter, an auditor who can hold office for a period of consecutive five yearsshall be appointed.
b) Conducting board meetings
At least one meeting should be conducted in every three calendar months. Four such meetings should be held every calendar year. The Chairman of the said meeting signs the minutes of the meeting.
c) Filing financial statements and annual returns
Private Limited Companies are required to file its Annual Accounts and Returns disclosing details of its shareholders, directors, etc., to the Registrar of Companies. Such fillings are required to be made once in a year, usually before September 30.
d) Maintainingstatutory registers and records
A Private Limited Company has to maintain various statutory registers and records as required by the Company law such as Register of shares, Register of Members, Register of Directors, etc. Besides, Incorporation documents of the company, Resolutions of the meetings of the Board of Directors, Minutes of the Board Meetings and Annual General Meeting, etc., are also required to be preserved by the company.
3) Audit compliances
The purpose of a statutory audit is to determine whether an organisation is providing a fair and accurate representation of its financial position by examining information such as bank balances, bookkeeping records, and financial transactions. Compliances related to audit include appointment of the statutory auditors of the company and finalising annual accounts with the auditors of the company.
4) Payroll compliances
It is obvious that you will have employees working for you when you start an organisation. There will be employees, independent consultants, and contractors as well. Such professional relationships are governed by various labour legislations. For instance, a business with an employee strength of over 20 needs to comply with ESI and PF regulations.
5) Taxation
A business has to pay taxes to the Central/State government or local bodies. Thus, every new entrepreneur should have the know-how of the aspects of taxation. Tax laws vary with sector and any recent changes should be within an entrepreneur's radar.
Tax compliance measures vary with the kind of business and the nature of services. A company selling goods would need to comply with the state VAT laws. Similarly, businesses working as service providers need to obtain service tax registration, make service tax payments, and file service tax returns on time. The business should also comply with relevant income tax rules and regulations.
The Comparison chart will give you a clear distinction between the compliance requirements of all the three forms of business.
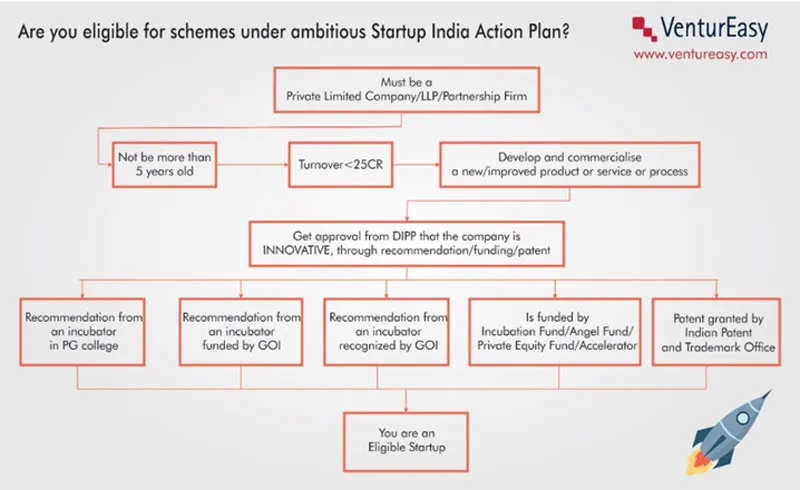
How Startup India Plan is easing norms
The ambitious Startup India Plan aims to simplify compliance, exempting tax on profits for the first three years, and rolling out an action plan for boosting innovation and entrepreneurship in the country. However, these benefits are applicable to companies, who have been approved as “Startup” by the inter-ministerial board, upon satisfaction of criteria as described below,
(Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the views of YourStory.)







